What is SD-WAN?
SD-WAN, short for Software-Defined Wide-Area Networking, is a technique that uses software to define and establish connections for wide-area networks (WANs), making them smarter and more flexible.
SD-WAN helps establish WAN connections between branches through wide-bandwidth commercial internet connections instead of relying solely on expensive leased channels (typically based on costly MPLS technology). Additionally, SD-WAN allows for centralized management of configurations and access policies for all branches, eliminating the need for manual management of individual WAN devices.
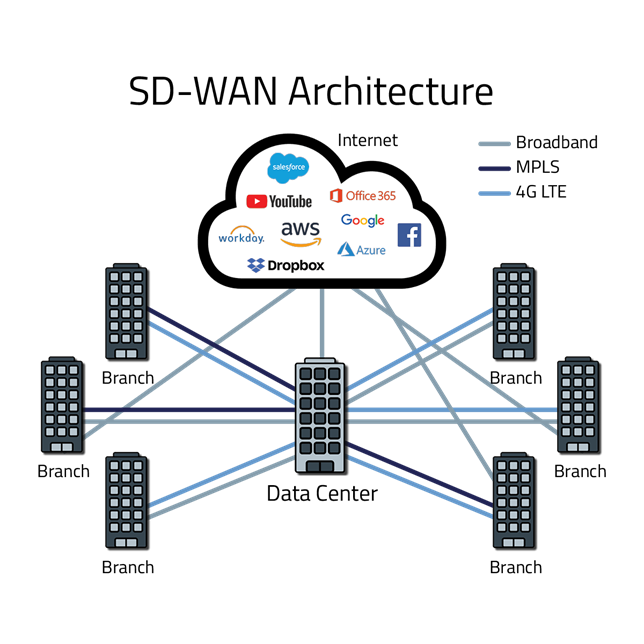
Why is SD-WAN important?
Digital transformation makes use of modern applications and cloud computing technologies increasingly popular. Its purpose is to create a foundation for new business methods that are causing significant changes in every economic and social field.
The first challenge of digital transformation lies in ensuring that organizations and businesses provide their increasingly dispersed workforce with secure and fast access to the system anytime, anywhere. Unfortunately, traditional connectivity methods often hinder digital transformation by separating and isolating offices and branches.
Today, organizations and businesses need agile, flexible, and cost-effective IT solutions if they want to compete effectively. They need solutions that are easy to implement, highly scalable, and able to meet the growing and changing demands every day. Moreover, in a world where downtime can greatly affect reputation and business results, businesses need to ensure that the network solutions they choose are always available.
SD-WAN is considered a solution that can harmoniously solve this problem. In particular, these new methods also bring additional benefits to businesses such as flexible scalability and enhanced system security. That is why SD-WAN is currently one of the most popular network solutions.
Key features of SD-WAN
- High availability: SD-WAN provides flexibility to minimize network downtime. The technology must have real-time detection of connection loss and automatically switch to another connection to operate.
- Quality of Service (QoS): SD-WAN supports QoS by prioritizing application levels and allocating bandwidth to the most important applications. SD-WAN will select dynamic connection routes, sending applications on faster routes or even splitting applications running on both routes to improve performance.
- Security: Compared to MPLS, SD-WAN leverages security tools (IPSEC) for authentication, monitoring, and encryption of connection channels.
- Management and troubleshooting: SD-WAN provides a prioritized graphical user interface (GUI) over a command-line interface (CLI) to allow administrators to choose automatic routing, configure and manage devices centrally.
- Load balancing: With a global view of network status, SD-WAN performs load balancing techniques to distribute network traffic by requesting new routing based on the current network condition to provide the best user experience.
The Vendor provides SD-WAN solutions


 Vi
Vi